
* The lower back, or lumbar spine, has 5 vertebrae, labeled L1-L5. * The upper back, or thoracic spine, has 12 vertebrae, labeled T1-T12. They also protect the spinal cord, nerves and arteries that extend from the brain to the rest of the body. The seven vertebrae of the cervical spine are responsible for the normal function and mobility of the neck. * The top 7 vertebrae that form the neck are called the cervical spine and are labeled C1-C7. By adulthood, we typically have 24 due to the fusion of the vertebrae in the sacrum. Humans are born with 33 separate vertebrae. When the spine is injured and its function impaired, the consequences may be painful and even disabling. Loss of spinal balance can result in strain to the spinal muscles and spinal deformity. The normal adult spine is balanced over the pelvis, requiring minimal workload on the muscles to maintain an upright posture. Its anatomy is extremely well designed, and serves many functions, including:Īll of the elements of the spinal column and vertebrae serve the purpose of protecting the spinal cord, which provides communication to the brain and mobility and sensation in the body through the complex interaction of bones, ligaments and muscle structures of the back and the nerves that surround it.
#Parts of spine professional#
Then you can work to optimize your movement to the best of your ability.Īuthor: Annie Beth Donahue is a professional writer with a health and disability focus.The spinal column is one of the most vital parts of the human body, supporting our trunks and making all of our movements possible. It is good to talk to your doctor about your function to determine what types of signals your body has the capability of sending and receiving. Sometimes people even lose voluntary motion in a body part but still retain reflex motion.Įvery injury is unique. Some people have partial injury, where they still have nerves that are working below the injury, and some people have complete injury. The areas affected are the parts of the body that connects to the spinal cord at the level of the injury or lower. That is why a spinal cord injury causes loss of movement, sensation, and reflexes. When the spinal cord is damaged, it prevents these signals from being sent correctly. Once it gets back to the starting point, the signal causes the muscle to react by squeezing or contracting. When the signal reaches the spinal cord, it goes back through at the same level it came in, returning to the muscle that initiated the signal. This triggers the nerves to send a message to the spinal cord. Reflex signals are initiated when the nerves in a muscle are irritated by being stretched or pushed on. They do not have to wait to reach the brain and then wait for the brain to choose a reaction. Reflex signals are designed to protect your body. Once they reach the spinal cord, they loop through and go straight back to the body part they came from. Reflex signals that cause movement do not come from your brain.Ī reflex signal comes from the nerves in your body, like sensory signals, but instead of going to your brain, they stop at the spinal cord. A muscle spasm is a good example of this type of movement. This means that the movement was not conscious. Reflex signals cause involuntary movements. An example of this would be when you reach out to hug someone. In fact, you don’t even realize you are consciously choosing to send the message to your body to move. These signals also occur so quickly that you feel like your body gets the message instantaneously. From there, they travel through the spinal cord, out to the spinal nerves, and then on to the parts of the body. These signals don’t begin at the nerve endings they begin inside the brain. These signals are not like sensory signals.
#Parts of spine how to#
The signals also tell your muscles specifically when and how to move. They tell your muscles to move when you want them to. They are the reason you can reach out with your arm and move the right distance to grab something without going too far or coming up short.
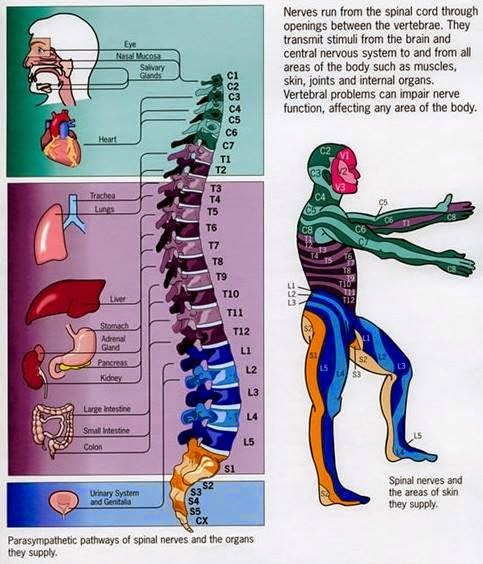
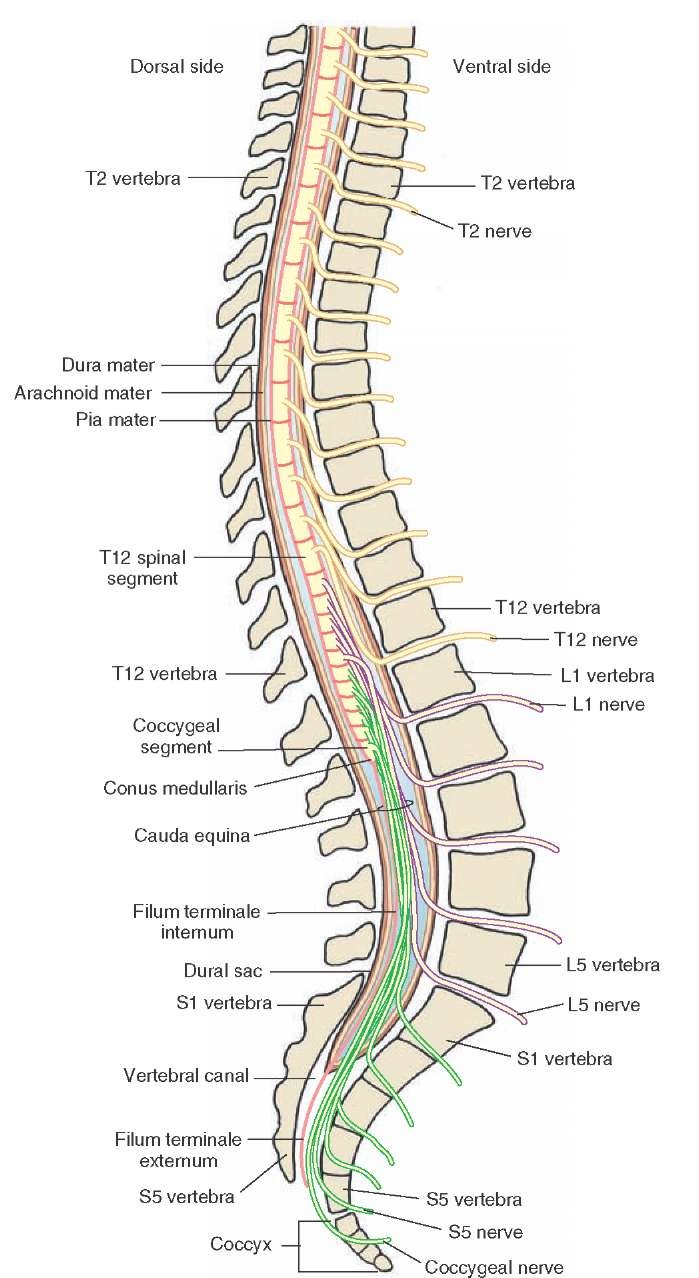
They also tell you where your body parts are in relation to the rest of your body. That means it tells you if you are standing, sitting, leaning, etc. Sensory signals travel so fast that it seems like you get the message instantaneously.Īnother thing that sensory signals do is they tell your brain what your body position is in space. Once the signals reach your brain, your body registers the sensation, and you are able to feel it. The nerves in the body send signals along their pathway to the spinal cord, then to the brain. These signals tell us when we are hot or cold, injured or safe. These feelings include temperature, touch, pain, and pressure. Sensory signals alert us to feelings both inside and outside the body.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
